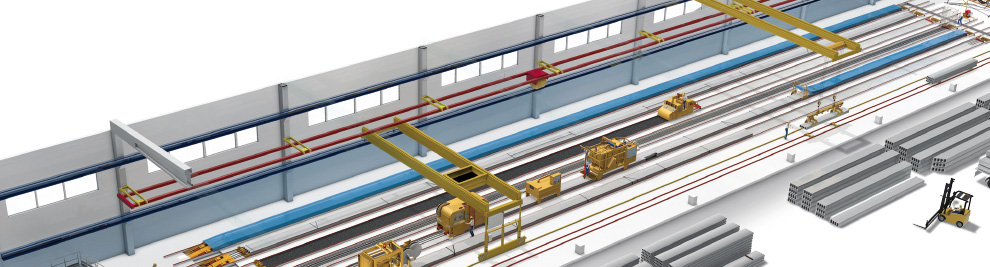
Manufacturing Process
Nordimpianti offers a wide range of production plant to satisfy all requirements ranging from small to large manufacturing output.
Production factories are set out in a logical order, with production phases appropriately scheduled to achieve maximum efficiency with low production costs.
These phases are:
- CLEANING AND OILING OF THE PRODUCTION BED
- LAYING OF THE STEEL WIRES OR STRANDS
- STRESSING OF THE STEEL WIRES OR STRANDS
- CONCRETE TRANSPORT AND DISTRIBUTION
- CONCRETE CASTING
- ELEMENT MARKING
- FRESH CONCRETE WORKING
- CONCRETE CURING
- DETENSIONING OF THE STEEL WIRES AND STRANDS
- ELEMENT CUTTING
- TRANSPORTATION OF THE ELEMENTS FOR STOCKING
The production phases should be organized over a 24 hour cycle taking into account the production quantity desired and the climatic conditions.
The production beds on which the elements are formed have an optimal length of between 120 to 150 m with widths varying from 1.5 to 2.6 m.
The speed of the casting machine on the production bed varies between 1-3 mpm, according to the types of element being produced.
Cleaning and Oiling of the production bed
A certain amount of concrete waste remains on the production beds once the manufactured elements have been removed. Therefore the beds must be thoroughly cleaned before re-using them.
This could be carried out manually using a broom, a shovel and a wheel barrow but would take a considerable waste of time.
The best solution is to use a cleaning machine that moves along the production bed removing debris and water.
A special oil sprayer is situated at the back of the machine and evenly sprays a fine film of detaching oil on to the surface of the production bed.
By the time the machine has reached the end of the production bed it is once again ready for re-use.
Laying of the steel wires or strands
After the cleaning and oiling of the bed a wire drawing trolley can pull the steel wires along the bed.
The cross section and the quantity of the steel wires to be positioned depends on the type of the concrete elements being produced and the load bearing requirements.
The steel wires are taken from the coils placed within the appropriate stackable decoilers and placed at the pulling head of beds.
Stressing of the steel wires or strands
The reinforcing steel wires have to be put in tension and fixed to the pulling head of the production bed before concrete casting.
The tensioning operation can be done in two ways, single wire or multi-stressing:
Single wire stressing: This tensioning operation is done with a wires stressing machine composed of a hydraulic central unit and a stressing jack, which with its conical indented metal rod catches each wire pulling them to a pre-determined tension.
An electronic control device interrupts the tensioning operation once each wire reaches the pre-determined necessary number of kN required.
Multi-stressing: This tensioning operation is done with a multi-stressing machine composed of a 2 big hydraulic cylinders which pull a movable anchor where all wires have been fixed.
In this way all the wires are tensioned simultaneously in one operation.
In both cases the prestressing wires or strands are fixed at the reaction beams with appropriate anchor grips.
Concrete transport and distribution
The concrete transport from the batching plant to the casting machine can be carried out in different ways depending on the customer’s requirements and the factory layout.
The most economical and quickest method is to use a bucket hooked to a overhead crane.
In cases where quick and high volume production is required it is possible to use a flying bucket and a concrete distributor which follow the casting machine along the production bed reducing the time needed to deliver the concrete.
Concrete Casting
When the production bed has been cleaned, oiled and with prestressing wires in tension, the casting machine is brought onto the bed ready to start the element casting.
Depending on the type of concrete element being produced the casting phase can be performed by one of three NORDIMPIANTI casting machines evo Extruder, sf Slipfomer or wf Wet Casting machine.
 Extruder:
Extruder:
The machine works with a semi-dry concrete and form the element by means of a extrusion method.
The Extruder machine can be fitted with various forming inserts according to the height of element that is to be produced.
 Slipformer:
Slipformer:
The machine works with a semi-dry concrete and form the element by means of a moulding-vibrating-pressing-finishing action.
The Slipfomer machine can be fitted with various forming inserts according to the element that is to be produced.
 Wet Casting machine:
Wet Casting machine:
The machine works with a semi-fluid concrete and form the element by means of a moulding-vibration-finishing action.
The Wet Casting machine can be fitted with various finishing moulds according to the element that is to be produced.
In all cases the casting machine is constantly supplied with concrete over the whole length of the bed.
The illustrations show the production phase of various elements. In particular it is possible to see the high level of compaction achieved by the machine as demonstrated by the fact that the element can support the weight of a person immediately after casting .
This does not apply to the Wet Casting machine which works with wet concrete.
Element marking
Element marking is widely used to print product information or mark out lines on the concrete elements.
Product information may be product data such as name and logo of manufacturer, date of production, product length, batch code or the type of stressing wires used.
Mark out lines may be used for cut lines, drawing out wet working templates or to meet the end users specific requirements.
These operations can be achieved by machines equipped with an inkjet printer head.
The ink used for the printing is waterproof and can be applied immediately after casting when the concrete is still wet or when the concrete is dry, before the cutting phase.
Fresh concrete working
The concrete elements may require notches, holes and breaks according to the design of the building.
This operation can be carried out by a special machine that sucks up concrete from the element whilst the concrete is still wet.
The removed concrete is deposited within a container that can be easily and quickly emptied.
Concrete Curing
Once the concrete casting has been completed, it needs a certain amount of time to reach the resistance of 350 Kg/sqcm before the steel wires can be released.
If there is no problem regarding the production volume required the elements are left to dry in the production beds; This takes from 24-72 hours depending on local temperature conditions and element sizes.
However if the number of production beds is limited and daily production output needs to be maximized it is possible to shorten the curing time by using an heating plant. Curing times can be shortened to 6-8 hours, after which the stressing wires can be released and the production beds can be made ready for another casting.
However it is always advisable to check the resistance of the concrete before wire detensioning using a cube test or smooth hammer device.
The concrete curing can be achieved in different ways. The most common method is the hot water system.
Other heating methods such as superheated steam or diathermic oil are pumped into heating pipes laid under the production beds in a closed circuit system.
During the curing it is advisable to use covering sheets on the elements in order to limit the rate of water loss from the concrete.
Detensioning of the steel wires and strands
When the concrete has reached the required strength to counteract the retracting of the internal prestressing wires, they are released.
Detensioning can be achieved in different ways depending on the stressing method used, single or multi.
With single wire stressing the detensioning is done by actiong on the detensioning cylinders, that contrast the mobile part of the reaction beams detensioning side, with the detensioning pump unit.
With multi stressing, the detensioning is achieved by means of the same cylinders that initially stressed the wires, releasing the anchor where the wires are fixed.
Element cutting
On the production bed the concrete is formed as a continuous element by the casting machine along the entire length of the bed. A cutting saw is then used to cut the elements into the required lengths.
The saw is moved along the bed and is positioned at the desired cutting point where the element is to be cut using a diamond blade. Cuts can be transversal, angular or longitudinal at any point along the element depending on the cutting machine used.
The amount of time needed to make a cut varies between 1-6 min. according to the kind and height of element to be cut.
During the cutting phase the blade is continuously cooled by a jet of water either from an onboard tank or through a tube wound round a motorized cable reel and connected to a tap at the end of the bed.
Transportation of the elements for stocking
After the elements are cut on the production beds they are ready to be lifted and transported to the stocking area. A special clamping equipment is used for lifting and transportation operation.
These clamps can be hooked onto the overhead crane or onto a special mobile lifting machine independently powered. This machine runs along the production bed, lifts the cut concrete elements off the production bed and deposits them outside at the head end of the Factory.
The elements are then taken to the end of the factory where they are transported to the designated stocking area by overhead crane or forklift trucks and stacked. These forklifts are also used to load the delivery trucks.
Of course, the elements can also be moved by using special wagon trolleys or tower cranes depending on the kind of internal organization.















 Contact Us
Contact Us